What is Cell Disease?
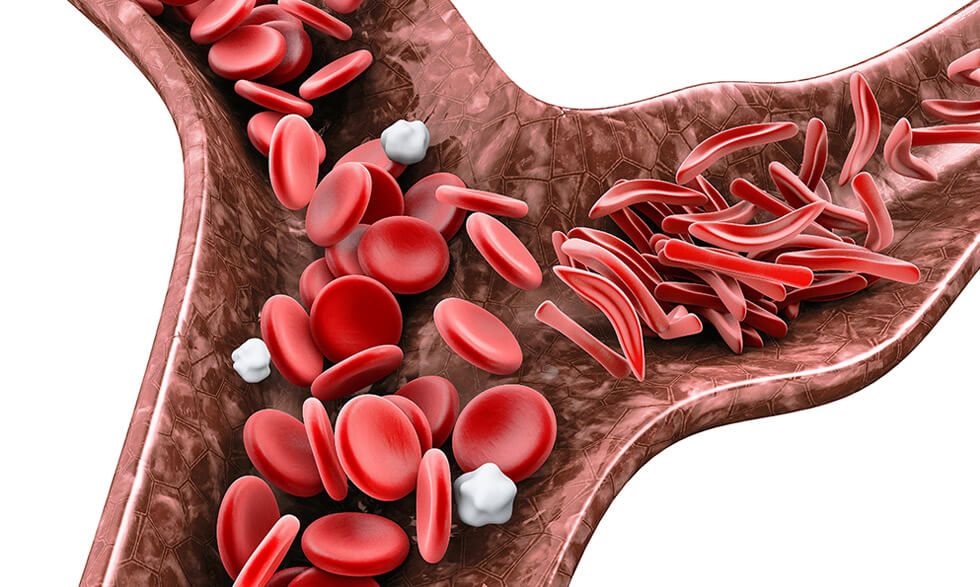
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a group of inherited red blood cell disorders. It is caused
by a problem with hemoglobin, which carries oxygen in the blood. The abnormal
hemoglobin causes the red blood cells to get sickle-shaped uniondemocrat.marketminute, or c-shaped. They can’t
move easily through the small blood vessels that carry oxygen to the rest of the
body. They get stuck and cause pain. People with SCD often have episodes of severe
pain, called pain crises. These can be very serious and need to be treated in the
hospital.
People with sickle cell disease might also have problems that can’t be treated at
home, like infections and problems in the lungs. This can be because of a lack of
oxygen and is the main cause of death in children and adults with sickle cell anemia.
It can lead to problems with the lungs called sickle chest syndrome, which means
high blood pressure in the lungs and scarring (pulmonary fibrosis). It can also cause
a serious complication that affects men with sickle cell disease, called priapism,
which is a painful erection.
In addition to causing pain and complications, anemia in people with sickle cell
disease can make them feel tired all the time. They might have trouble keeping up
with their schoolwork or work, and they can also have a slow heart rate, which can
be life-threatening. Babies and young children with sickle cell disease may be fussy
or irritable and may not grow as quickly as other kids their age.
There are many treatments for sickle cell disease. These include medicines and
blood transfusions. In some cases, a stem cell transplant might cure sickle cell
anemia.

Treatment is aimed at avoiding painful episodes, relieving symptoms, and
preventing complications. The medicines most often used are hydroxyurea (Droxia,
Hydrea, Siklos) and L-glutamine oral powder (Endari). Hydroxyurea can reduce the
frequency of pain episodes and might also decrease the need for repeated blood
transfusions. But it can increase the risk of infections, and it shouldn’t be taken by
pregnant women. L-glutamine might help prevent and treat pain episodes by
reducing the amount of oxygen needed by sickled red blood cells to pass through
the lungs. It is taken as a capsule once a day.
Many states screen babies for sickle cell disease at birth so that they can receive
early treatment to prevent serious complications. A routine test can detect the
condition, as well as other genetic diseases. A blood test called hemoglobin
electrophoresis can check for the type of abnormal hemoglobin that causes sickle
cell disease.
Sickle cell disease is more common in people of African American descent, but it can
happen to anyone. About one in 365 Black babies is born with sickle cell disease,
and it can also affect people of Hispanic, Mediterranean, South American, or Middle
Eastern descent. The only way to prevent sickle cell disease is to not inherit the
gene for it. People can find out if they have the gene for it by getting a blood and
urine test before pregnancy.
